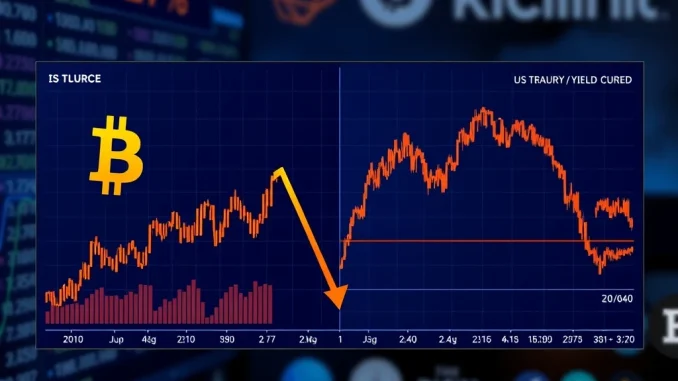
NEW YORK, March 2025 – The widening spread between 2-year and 30-year US Treasury yields has reached its highest level since 2021, creating significant downward pressure on Bitcoin prices as traditional financial dynamics increasingly influence cryptocurrency markets. This development marks a crucial moment where macroeconomic forces directly impact digital asset valuations, particularly affecting non-yielding assets like Bitcoin during periods of rising interest rates.
Understanding the US Treasury Yield Spread Mechanism
The Treasury yield spread represents the difference between short-term and long-term government bond interest rates. Typically, a normal yield curve shows higher rates for longer maturities. However, when this spread widens dramatically, it signals important economic shifts. Currently, the 2-year to 30-year spread has expanded to levels not seen in four years, indicating rising long-term yield expectations.
David Roberts, head of fixed income at Nedgroup Investments, explains this phenomenon clearly. “A widening Treasury spread signifies rising long-term yields,” Roberts states. “This movement reflects market expectations about future inflation and economic growth patterns.” The recent sell-off in Japanese government bonds has contributed significantly to this trend, creating ripple effects across global bond markets including US Treasuries.
How Rising Yields Impact Bitcoin Valuation
Higher interest rates create substantial challenges for non-yielding assets like Bitcoin. When traditional investments offer attractive returns with perceived lower risk, capital naturally flows toward these opportunities. This dynamic creates several specific pressures on cryptocurrency markets:
- Opportunity Cost Increases: Holding Bitcoin becomes more expensive when safe government bonds offer meaningful yields
- Risk Appetite Shifts: Investors rebalance portfolios toward less volatile assets during uncertain periods
- Liquidity Redistribution: Capital moves from speculative assets to income-generating instruments
- Volatility Sensitivity: Assets without fundamental yield become more vulnerable to market sentiment shifts
Roberts emphasizes this connection directly. “Higher interest rates increase the burden of holding non-yielding assets,” he notes. “This makes volatility-sensitive assets like Bitcoin more likely to face downward price pressure.”
Historical Correlation Patterns Between Bonds and Bitcoin
Historical data reveals consistent patterns between bond market movements and cryptocurrency valuations. During the 2018 rate hike cycle, Bitcoin experienced significant declines as Treasury yields rose. Similarly, the 2021-2022 period showed inverse correlations between bond yields and cryptocurrency prices. The current widening spread suggests these historical patterns may be repeating.
The following table illustrates key historical correlations:
| Period | Treasury Spread Movement | Bitcoin Price Reaction | Correlation Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2017-2018 | Spread narrowing from 125bp to 25bp | BTC fell 70% from peak | Strong inverse correlation |
| 2020-2021 | Spread widening during pandemic | BTC rose 400% | Positive correlation initially |
| 2022-2023 | Rapid spread inversion | BTC declined 65% | Strong inverse correlation |
| 2024-2025 | Current widening trend | BTC showing pressure | Developing inverse pattern |
Global Bond Market Dynamics and Crypto Implications
The current Treasury spread widening doesn’t occur in isolation. Global bond markets demonstrate interconnected movements that collectively impact cryptocurrency valuations. Japanese government bond sell-offs have particularly influenced recent Treasury yield increases. As the Bank of Japan adjusts its yield curve control policies, international investors reallocate capital, affecting US Treasury markets directly.
This global context matters significantly for Bitcoin investors. International capital flows increasingly consider cryptocurrency as part of broader portfolio allocations. When traditional fixed income becomes more attractive globally, cryptocurrency allocations often face reduction. This creates a compounding effect where multiple bond market movements simultaneously pressure digital assets.
Expert Analysis on Sustained Yield Increases
Financial analysts emphasize the importance of duration in this relationship. Temporary yield increases may cause minor Bitcoin price adjustments, but sustained higher rates create more significant challenges. Roberts specifically addresses this duration factor. “A sustained increase in long-term yields could adversely affect Bitcoin,” he assesses. This perspective highlights how timeframes matter when analyzing bond-crypto correlations.
Market participants should monitor several key indicators to gauge potential duration:
- Federal Reserve communications regarding future rate policy
- Inflation data trends across major economies
- Global central bank coordination on monetary policy
- Bond market liquidity conditions and trading volumes
Cryptocurrency Market Structural Vulnerabilities
Bitcoin’s specific characteristics make it particularly sensitive to interest rate environments. Unlike dividend-paying stocks or coupon-paying bonds, Bitcoin generates no income stream. This structural difference becomes crucial during rising rate periods. Additionally, Bitcoin’s volatility profile amplifies sensitivity to macroeconomic shifts.
The cryptocurrency market’s relative youth compared to traditional finance creates additional vulnerability. With less historical data on performance during various rate environments, investors face greater uncertainty. This uncertainty often translates to precautionary selling when traditional markets show stress signals. The current Treasury spread widening acts as precisely such a signal.
Institutional Investor Behavior Patterns
Institutional participation in cryptocurrency markets has grown substantially since 2020. These investors typically employ sophisticated risk management frameworks that automatically adjust allocations based on macroeconomic indicators. Treasury yield spreads feature prominently in many institutional risk models.
When spreads widen beyond certain thresholds, algorithmic trading systems often reduce exposure to volatile assets. This creates systematic selling pressure that compounds individual investor decisions. The increasing institutionalization of cryptocurrency markets therefore amplifies traditional financial correlations.
Potential Mitigation Factors and Countervailing Forces
Despite the downward pressure from widening Treasury spreads, several factors could mitigate Bitcoin’s decline. Adoption growth continues across both retail and institutional segments. Technological developments like the Lightning Network improve Bitcoin’s utility as a payment system. Regulatory clarity in major markets may increase investor confidence despite rate pressures.
Additionally, Bitcoin’s fixed supply characteristic provides inherent scarcity value that traditional fiat currencies lack. During periods of high inflation, this scarcity can offset some interest rate pressures. The current environment features both rising rates and persistent inflation concerns, creating competing influences on Bitcoin valuation.
Conclusion
The widening US Treasury yield spread creates significant downward pressure on Bitcoin prices through multiple transmission mechanisms. Higher long-term yields increase the opportunity cost of holding non-yielding assets while shifting investor risk preferences toward less volatile instruments. As global bond markets experience coordinated movements, cryptocurrency valuations face increasing influence from traditional financial dynamics. Market participants must monitor Treasury spread developments alongside cryptocurrency-specific factors to navigate this complex intersection of traditional and digital finance effectively.
FAQs
Q1: What exactly is the US Treasury yield spread?
The Treasury yield spread measures the difference between short-term and long-term government bond interest rates. Specifically, it often compares 2-year and 30-year Treasury yields to gauge market expectations about future economic conditions.
Q2: Why does a widening yield spread affect Bitcoin?
A widening spread typically indicates rising long-term interest rates, which increases the opportunity cost of holding non-yielding assets like Bitcoin. Higher rates make income-generating investments more attractive relative to speculative assets.
Q3: How long do these effects typically last?
The duration depends on how sustained the yield increase proves to be. Temporary spikes may cause short-term volatility, while prolonged higher rates create more persistent pressure on cryptocurrency valuations.
Q4: Are all cryptocurrencies affected equally?
No, different cryptocurrencies respond differently. Bitcoin, as a non-yielding store of value, shows stronger correlation with interest rates. Yield-generating DeFi tokens or stablecoins may demonstrate different sensitivity patterns.
Q5: What should Bitcoin investors monitor during this period?
Investors should track Federal Reserve policy statements, inflation data releases, global bond market movements, and cryptocurrency market liquidity conditions to assess potential duration and severity of pressure.